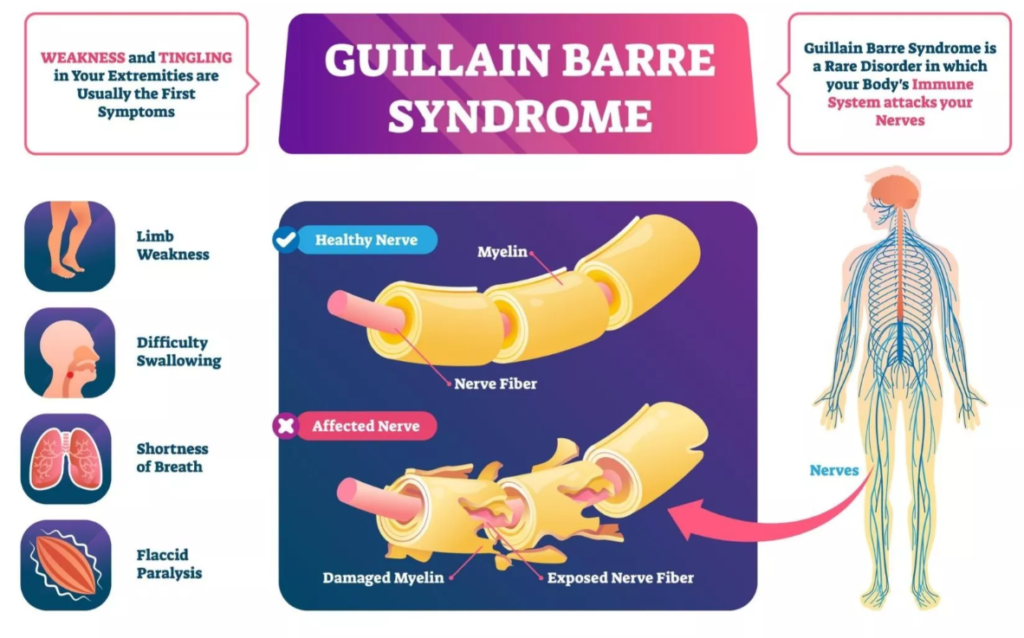
What is Guillain Barre Syndrome
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is a rare disease that attacks the body's peripheral nervous system. GBS is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks nerve cells in the peripheral nervous system. As a result, inflammation of the peripheral nerves occurs which causes neurological dysfunction and various symptoms.
Causes of Guillain Barre Syndrome
The exact cause of Guillain Barre Syndrome is not fully understood, but GBS is often associated with a viral or bacterial infection in the patient. Several infections that are known to play a role in causing GBS include upper respiratory tract infections, measles, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Symptoms of Guillain Barre Syndrome
The initial symptoms of GBS are usually weakness or numbness that begins to appear in the extremities. This weakness can spread to other parts of the body within days or weeks. Some other common symptoms include:
- Difficult to walking or standing.
- Difficulty moving the eyes or face.
- Difficulty swallowing and speaking.
- Muscle ache.
- Coordination and balance disorders.
- Irregular heartbeat.
As sufferers develop increasingly severe symptoms, paralysis can occur throughout almost the entire body, including the lungs. In severe cases, a person may need to be admitted to an intensive care unit for life-threatening breathing problems.
The Process of Guillain Barre Syndrome
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system attacks nerve cells in the body's peripheral nervous system. There are many factors that are thought to contribute to the development of this disease. The course of GBS can be described as follows:
- Infections or Triggers
GBS is usually triggered by a viral or bacterial infection that the sufferer has recently experienced. Some infections associated with GBS include upper respiratory tract infections, measles, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Although it is not yet known for certain, this infection is thought to trigger an excessive immune response, causing the immune system to attack nerve cells in the peripheral nervous system.
- Autoimmune response
After an infection or other trigger, the immune system begins to make antibodies to fight the pathogen. However, in some cases of GBS, the immune system also produces antibodies that attack nerve cells in the peripheral nervous system. These antibodies target myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds nerves, as well as axons, the nerve's electrical transmitters. This attack causes these nerves to become inflamed, which disrupts their normal function and causes GBS symptoms.
- Inflammation and nervous disorders
Inflammation occurs in the nerves due to an autoimmune attack that disrupts the transmission of electrical signals to and from the muscles and organs of the body. This causes symptoms such as muscle weakness, numbness, and sensory disturbances in the feet, hands, and other parts of the body. In addition, nerve disorders that control autonomic functions such as heart rate, blood pressure and the digestive system can also occur.
- Disease progression
GBS symptoms usually come on quickly and peak within a few weeks. The inflammatory process and resulting nerve damage can continue for weeks or months, depending on the severity of the disease. In some cases, symptoms can be severe and affect your ability to breathe, requiring emergency medical treatment.
The Impact of Guillain Barre Syndrome in Daily Life
The following are some of the effects that may occur and affect a person's daily life, especially during the acute phase of the disease and the recovery phase:
- Weaknesses, physical limitations
One of the main symptoms of GBS is muscle weakness which can be very serious. People with GBS may have difficulty walking, standing, or doing other physical activities. These limitations can interfere with daily mobility, including moving from one place to another, climbing stairs, or doing activities outside the home.
- Depend on the help of others
People with very weak GBS may need help from others to carry out daily activities. They may need help walking, bathing, dressing, or performing other tasks they were previously able to do independently.
- Sensory disturbances
Apart from muscle weakness, GBS can also cause sensory disorders such as numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in certain parts of the body. This can interfere with the patient's comfort and ability to feel touch or temperature.
- Impaired autonomic function
GBS sufferers can also experience autonomic dysfunction, such as changes in blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, difficulty swallowing, and digestive disorders. This disorder can be uncomfortable and affect the quality of daily life.
- Feeling tired and thirsty
The GBS recovery process can be very tiring. Sufferers of this disease often feel tired and weak, even when doing activities that were previously considered easy. Thirst can also be a problem because dehydration can occur if the person has difficulty swallowing.
- Social and emotional limitations
GBS can affect the social and emotional aspects of a patient's life. Physical and mobility limitations can make people feel isolated and dependent on others for help. This can cause feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Financial impact
GBS patients often require intensive care in hospitals or rehabilitation centers, which can result in high medical costs. In addition, physical limitations and work ability can affect income and result in additional financial burdens.
The Role of Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy has a very important role in the management of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) cases. physiotherapy helps speed recovery and optimize the patient's physical function during and after the acute phase of the disease.
- Improve muscle weakness
One of the main symptoms of GBS is muscle weakness which can cause physical limitations. Physiotherapy helps restore muscle strength by performing special exercises to increase muscle strength and endurance. These exercises are designed to suit the sufferer's level of weakness and ability.
- Improves balance and coordination
GBS can affect balance and coordination, so people with the condition may have difficulty walking or doing other activities steadily. Physiotherapists use special exercises to improve balance and coordination, so that patients can return to movement more safely.
- Increase mobility
Physiotherapy helps improve patient mobility, whether walking, standing, or doing other activities. Physiotherapy techniques and exercises help patients relearn good mobility and overcome any limitations that may arise.
- Prevents contractures
During the recovery period, GBS sufferers who experience muscle weakness tend to experience contractures, which is a condition where the muscles become stiff and limit joint movement. Physiotherapy can help prevent contractures by moving and massaging muscles to maintain their flexibility and flexibility.
- Critical period recovery
During the acute phase of GBS, people with the disease often require treatment in an intensive care unit and can experience severe disability. Physiotherapy can help treat and manage sufferers during critical periods, such as assisting with respiratory care and preventing further complications.
- Psychological support
Apart from physical benefits, physiotherapy can also provide psychological support for GBS sufferers. Physiotherapists help increase patient motivation, provide emotional support, and overcome anxiety or depression that may arise during the recovery period.
Also read: Cedera Saraf Dan Sistem Klasifikasinya
Reference :
- Nguyen TP, Taylor RS. Guillain-Barre Syndrome. [Updated 2023 Feb 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532254/
- Shah, Nehal & Shrivastava, Manisha. (2015). Role of Physiotherapy in Guillain Barre Syndrome: A Narrative Review. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences. 5. 529.
- Khan F, Amatya B. Rehabilitation interventions in patients with acute demyelinating inflammatory polyneuropathy: a systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012 Sep;48(3):507-22. Epub 2012 Jul 23. PMID: 22820829.
- Sulli S, Scala L, Berardi A, Conte A, Baione V, Belvisi D, Leodori G, Galeoto G. The efficacy of rehabilitation in people with Guillain-Barrè syndrome: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021 Apr;21(4):455-461. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2021.1890034. Epub 2021 Feb 23. PMID: 33567916.
- van Doorn PA, Ruts L, Jacobs BC. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2008 Oct;7(10):939-50. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70215-1. PMID: 18848313.