The Numeric Pain Rating Scale, or often referred to as NRS, is a measurement tool used in the medical world to measure the level of pain intensity or pain felt by a person. This scale is designed to help patients or individuals communicate the extent of the pain they feel to medical personnel or health care providers.
NPRS Instrument Population
Numeric Pain Rating Scale merupakan instrument yang digunakan untuk mengukur tingkat nyeri yang dirasakan seseorang. Secara umum, populasi dari instrument ini adalah :
- Chronic Pain
- Back Pain
- Spinal injury
- Non-specific patient population
NPRS Scoring System
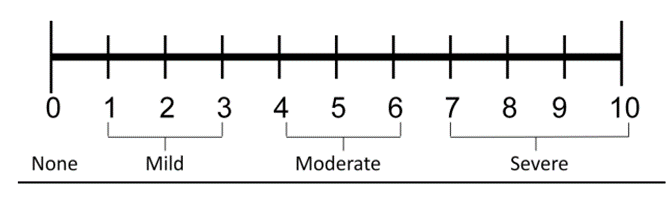
The Numeric Pain Rating Scale usually consists of integers from 0 to 10, with each number having a different meaning in describing the level of pain. Here is a general interpretation of the numbers in the Numeric Pain Rating Scale:
- 0 : No Pain – The patient feels no pain at all.
- 1-3 : Mild Pain – The patient feels very mild or almost no pain.
- 4-6 : Moderate Pain – The patient has acceptable, but manageable pain.
- 7–9 : Severe Pain – The patient feels pain that is intense and interferes with daily activities.
- 10 : Worst Pain Ever Experienced – The patient feels the most intense pain possible and is often referred to as the “worst pain ever experienced.”
How to Use NPRS
Patients are asked to provide or circle a number that reflects the level of pain they have felt in the last 24 hours, where 0 is no pain at all and 10 is the worst pain they have ever felt. The scores given by patients can help medical personnel or doctors determine appropriate treatment plans, including the use of painkillers or other medical procedures.
Reliability of the NPRS
| POPULATION | CRITERIA | MARK |
| Non-Specific Patient Populations | Interater/Intrarater reliability | Interrater reliability excellent with 100% agreement between two NPRS raters with 0-10 points |
| Internal Consistency | Excellent internal consistency for the NPRS in participants aged 65-94 years (Cronbach's alpha = 0.87) Excellent internal consistency for the NPRS in participants aged 25-55 years (Cronbach's alpha = 0.88) | |
| Chronic Pain | Test-retest reliability | Adequate reliability for a pair of assessments (one assessment at week 1, one assessment at week 2) (r = 0.63)Excellent reliability for assessments on 2 or more days during week 1 compared to 2 or more days during week 2 (r = 0.79 – 0.92) |
| Internal Consistency | Excellent internal consistency for two assessments (one on week 1 and one on week 2) (Coefficient alpha = 0.84) Excellent internal consistency for two assessments on 2 or more days during week 1 compared with 2 or more days during week 2 (Alpha coefficient = 0.89 –0.98) |
Validity of the NPRS
| POPULATION | CRITERIA | MARK |
| Spinal injury | Construct Validity | Adequate correlation between NPRS and Verbal Rating Scale (Spearman's r = 0.38) |
| Content Validity | In a vote regarding the validity and usefulness of the NPRS in people with SCI-related pain, participants voted as follows: 64% The NPRS is a valid measure and should be part of the minimum data set for a clinical trial 14% The NPRS is a valid measure but should be part of the expanded dataset only20% NPRS requires further study to establish reliability and validity before recommendingNPRS 2% not valid or relevant for use79% NPRS as first choice for minimum dataset over VRS (16%) and VAS (5%) (n= 57) | |
| Non-specific Population | Criterion Validity | Population of healthy people : Very good correlation between NPRS and VAS (r = 0.86) Very good correlation between NPRS and Verbal Descriptor Scale (r = 0.88) Very good correlation between NPRS and 21-point Numeric Rating Scale ( r = 0.87)Excellent correlation between NRPS (on a scale of 0-20) and Faces pain scale (r = 0.80) |
| Construct Validity | Emergency Room Population convergent validity Very good correlation between NRPS and VAS (r = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.93-0.95)) | |
| Face Validity | Population of healthy people: 35.3% prefer the 21-point Numeric Rating Scale (written format)25.3% prefer the Verbal Descriptor Scale15.9% prefer the NPRS (11-point verbal scale)12.9% prefer the Faces pain scale10 .6% preferred VASl |
Also read: Nyeri di Area Lutut Saat Berolahraga? Ayo Cari Tahu Penyebabnya
Reference :
- Haefeli M, Elfering A. Pain assessment. Eur Spine J. 2006 Jan;15 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17-24. doi: 10.1007/s00586-005-1044-x. Epub 2005 Dec 1. PMID: 16320034; PMCID: PMC3454549.
- Shirley Ryan Ability Lab. diakses pada 25 September 2023 pada https://www.sralab.org/rehabilitation-measures/numeric-pain-rating-scale
- PhysioPedia.Numeric Pain Rating Scale. Diakses pada 25 September 2023 melalui https://www.physio-pedia.com/Numeric_Pain_Rating_Scale