What is Osgood-Schlatter Disease (OSD)
Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) is an inflammatory condition that occurs at the insertion of the patellar tendon on the tibial tuberosity. The classic clinical picture of this condition is pain in the anterior knee and tenderness at the attachment point of the patellar tendon at the tibial tuberosity. This condition is usually self-limited and occurs as a result of stress from repetitive extensor biomechanics, such as jumping, running and going up and down stairs.
Osgood-Schaltter disease (OSD) usually occurs in the final phase of bone growth. OSD appears in boys at the age of 12 – 15 years, while in girls at the age range of 8 – 12 years. There are several risk factors for OSD, such as male gender, sudden bone growth and repetitive activities such as jumping and running.
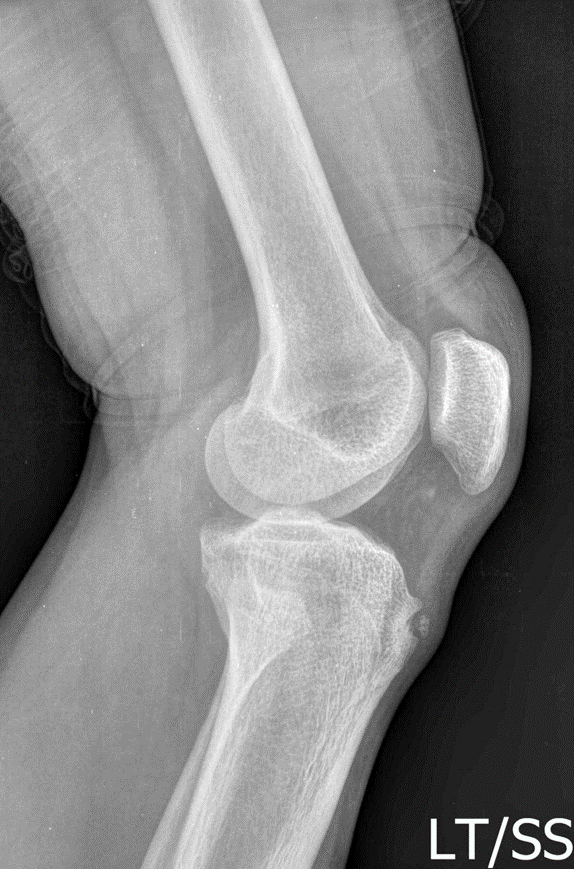
Vaishya R, Azizi AT, Agarwal AK, Vijay V. Apophysitis of the Tibial Tuberosity (Osgood-Schlatter Disease): A Review. Cureus. 2016
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms that generally appear in OSD conditions are:
- Pain on the anterior side of the knee
- There is tenderness in the anterior area of the knee
- Swollen
- The pain gets worse when used to run, jump and go up and down stairs.
Causes and How Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) Occurs
Osgood-Schaltter disease (OSD) is caused by traction apophysitis of the tibial tubercle due to repetitive strain and chronic avulsion of the secondary ossification center of the tibial tuberosity. This repetitive strain is caused by the strong pull of the quadriceps muscle produced during sporting activities. Avulsion of the tibial tuberosity can occur in the preossification phase or ossification phase at the secondary ossification center.
The tibial tubercle develops as a secondary ossification center that provides attachment to the patellar tendon. Bone growth that exceeds the ability of the muscle-tendon unit to stretch sufficiently to maintain its previous flexibility will cause increased tension across the apophysis. The physis is the weakest point in the muscle-tendon-bone attachment (in contrast to tendons in adults) and is, therefore, at risk of repetitive stress injury. With repeated contractions of the quadriceps muscle, especially repeated forced knee extension movements as seen in sports that require running and jumping (basketball, football, gymnastics), will result in softening and partial avulsion of the apophyseal ossification center, resulting in osteochondritis.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD)
The main goal of Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) management is to reduce pain and swelling in the knee. Patients should reduce their physical activity until symptoms begin to subside
Physiotherapy in this case plays a role in helping pain management and providing strengthening exercises. Strengthening exercises on the quadriceps, hamstring and gastrocnemius muscles are recommended in this case. The use of braces and casts for joint immobilization can also be applied to reduce tension on the tibial tuberosity.
Also read: Kenali Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reference :
- Smith JM, Varacallo M. Osgood-Schlatter Disease. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441995/
- Gholve PA, Scher DM, Khakharia S, Widmann RF, Green DW. Osgood Schlatter syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2007 Feb;19(1):44-50. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e328013dbea. PMID: 17224661.
- Vaishya R, Azizi AT, Agarwal AK, Vijay V. Apophysitis of the Tibial Tuberosity (Osgood-Schlatter Disease): A Review. Cureus. 2016 Sep 13;8(9):e780. doi: 10.7759/cureus.780. PMID: 27752406; PMCID: PMC5063719.